DxHF: Providing High-Quality Human Feedback for LLM Alignment via Interactive Decomposition [Paper][Code&Data]
Shi et al. UIST’25: Introduces a human-in-the-loop feedback method for improving LLM alignment. The approach decomposes user feedback into interpretable sub-tasks, guiding the LLM through interactive evaluation and refinement cycles.
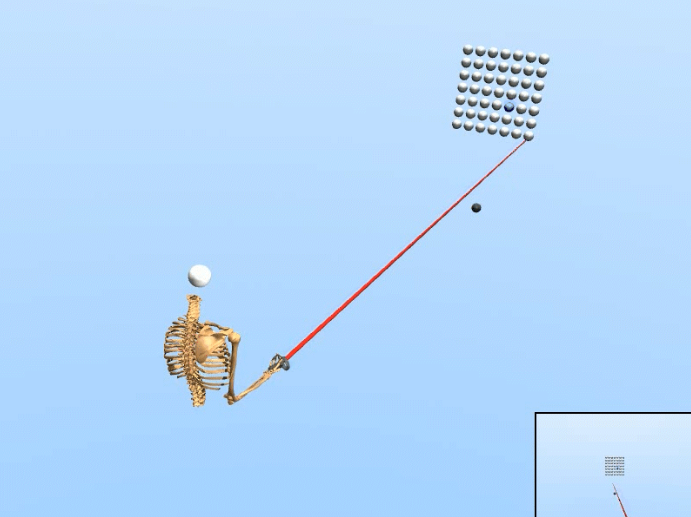
Real-time 3D Target Inference via Biomechanical Simulation [Paper][Code&Data]
Moon et al. CHI’24: Presents a biomechanical simulation model for real-time prediction of 3D movement targets. The model infers intended motion endpoints from partial kinematic data, improving interaction tracking in immersive systems.
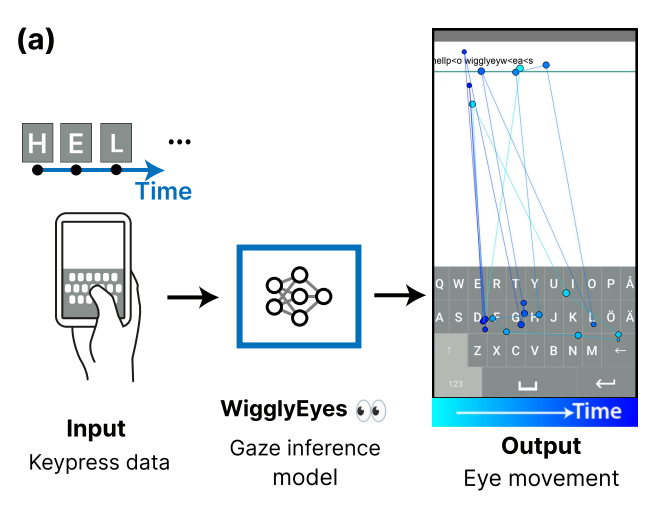
WigglyEyes: Inferring Eye Movements from Keypress Data [Code&Data]
Zhu et al. 2024: Proposes a novel method to infer eye movement patterns from typing behavior using keypress timing and sequence data. Enables eye-tracking inference without cameras, bridging typing and visual attention analysis.
In: arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.15669, 2024.
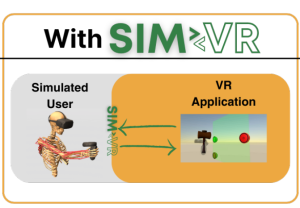
SIM2VR: Towards Automated Biomechanical Testing in VR [Code]
Fischer et al. UIST’24: Introduces a VR-based pipeline for automated biomechanical testing. The system simulates and evaluates user movement dynamics in virtual reality, using reinforcement learning and physics models to assess interaction ergonomics

Agent Forge: A Flexible Low-Code Platform for Reinforcement Learning Agent Design [Code&Data]
Fernandes & Oulasvirta, 2024: Introduces AgentForge, a modular low-code framework for rapid design and testing of reinforcement-learning agents. It streamlines experimentation, visualization, and model integration for UI and robotics research.
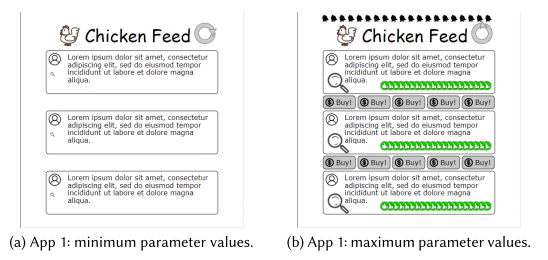
Cooperative Multi-Objective Bayesian Design Optimization [Data]
The paper introduces a cooperative multi-objective Bayesian optimization approach where designers and an optimizer jointly explore and refine design spaces. The method improves design quality while keeping humans actively involved in decision-making.
Interactive Reward Tuning: Interactive Visualization for Preference Elicitation [Paper]
Shi et al. IROS’24: Presents an interactive visualization tool for tuning reward functions in reinforcement learning. Users iteratively adjust and visualize preferences, enabling more interpretable and controllable AI behavior.
In: 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), IEEE 2024.
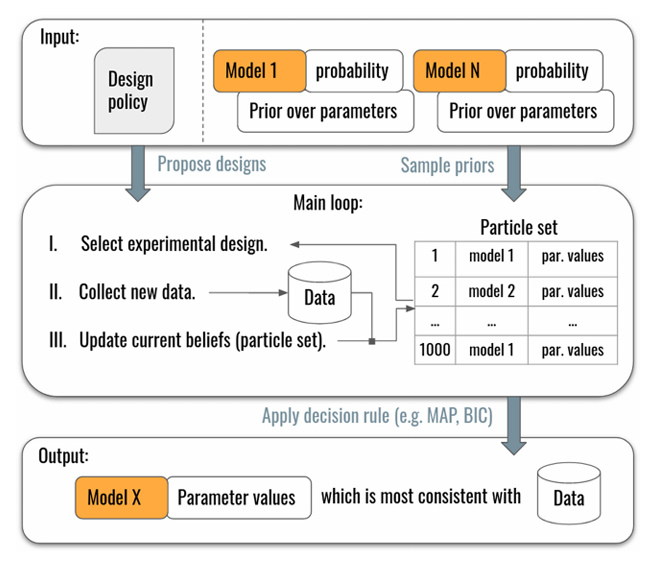
Online Simulator-Based Experimental Design for Cognitive Model Selection [Paper]
Aushev et al.’23 introduce an online simulator-based approach that adaptively designs experiments to efficiently distinguish between competing cognitive models. It enables faster and more informative model selection when model likelihood are intractable.
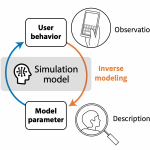
Amortized inference with user simulations (CHI’23) [Paper][Video]
Moon et al. CHI’23: Amortized Inference with User Simulations speeds up parameter estimation in simulation-based user models. Synthetic data sampled from model parameters train a neural density estimator that approximates the posterior over parameters from observations, enabling faster and scalable inference.

CoColor: Interactive Exploration of Color Designs [Paper][Pseudocode]
Hegemann et al. IUI’23: Introduces an interactive computational method for exploring and generating harmonious color designs. The system combines perceptual color metrics with algorithmic optimization, allowing users to iteratively refine color palettes through visual feedback and pseudocode-based generation.
In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Association for Computing Machinery, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2023, ISBN: 979-8-4007-0106-1/23/03.

AUIT – the Adaptive User Interfaces Toolkit for Designing XR Applications [Paper]
Belo et al. UIST’22: Introduces AUIT, an open-source toolkit for building adaptive interfaces in XR environments. The system supports dynamic adaptation of interface elements through modular design and user modeling, simplifying experimentation in VR/AR design research.
In: Proceedings of the 35th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Association for Computing Machinery, Bend, OR, USA, 2022, ISBN: 9781450393201.
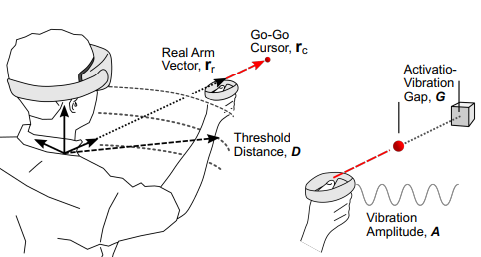
Investigating Positive and Negative Qualities of Human-in-the-Loop Optimization for Designing Interaction Techniques [Paper][Code]
Chan et al. CHI’22 study the human-in-the-loop Bayesian optimization for interaction design, comparing optimizer-assisted and designer-led workflows. While optimization helped designers find better solutions with less effort, it also reduced their sense of agency and creativity.
In: Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’22), ACM, 2022.

Responsive and Personalized Web Layouts with Integer Programming [Paper][Video]
Laine et al. PACMHCI’21: Proposes an integer programming method for generating responsive and personalized web layouts. The technique optimizes visual composition by balancing user preferences, device constraints, and aesthetic rules automatically.
Grid-based Genetic Operators for Graphical Layout Generation [Paper]
Shiripour et al. PACMHCI’21: Introduces genetic algorithms with grid-based operators for automated graphical layout generation. The approach evolves design layouts according to perceptual and usability fitness metrics, enabling creative co-design with AI.
In: Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, vol. 5, no. EICS, pp. 1–30, 2021.
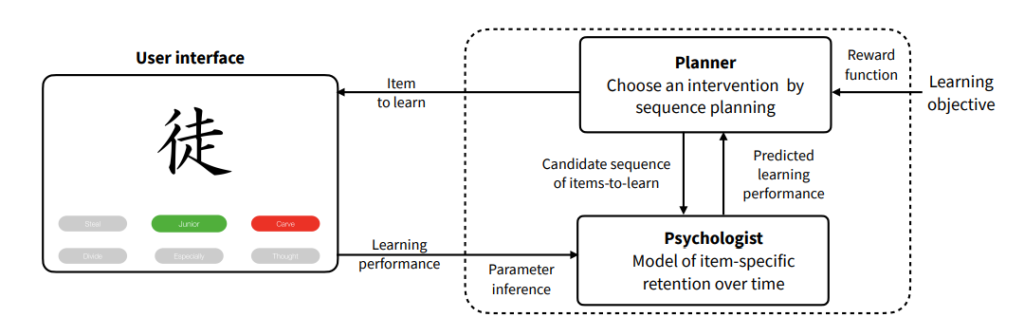
Improving Artificial Teachers by Considering how People Learn and Forget [Paper][Code&Data]
Nioche et al. IUI’21: Presents a computational model of learning and forgetting for adaptive tutoring systems. By modeling human memory decay, the artificial teacher optimizes lesson sequencing and feedback timing to improve user retention.
Adapting User Interfaces with Model-based Reinforcement Learning (CHI ’21) [Paper][Code][Video]
Todi et al. CHI’21 formulate UI adaptation as a stochastic sequential decision problem. Predictive HCI models simulate interface changes, and Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) with a value network plans adaptation sequences. The method balances user benefit versus surprise/relearning costs and uses offline-trained neural value estimators to accelerate online planning.
Fast Design Space Rendering of Scatterplots [Paper]
Santala et al. EuroVis’20: Presents a computational visualization method for rapidly rendering scatterplot design spaces. Using OpenCV and dynamic sampling, the system allows designers to visually explore large numbers of scatterplot variations efficiently.
In: Kerren, Andreas; Garth, Christoph; Marai, G. Elisabeta (Ed.): EuroVis 2020 – Short Papers, The Eurographics Association, 2020, ISBN: 978-3-03868-106-9.
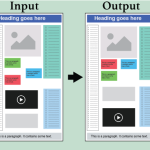
GRIDS: Interactive Layout Design with Integer Programming [Paper][Code&Data]
Dayama et al. CHI’20: Proposes GRIDS, an interactive design tool that applies integer programming to graphical layout creation. The system optimizes layout structure while allowing designers to explore alternatives interactively, combining human creativity with algorithmic precision.
In: Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ’20), ACM, 2020.
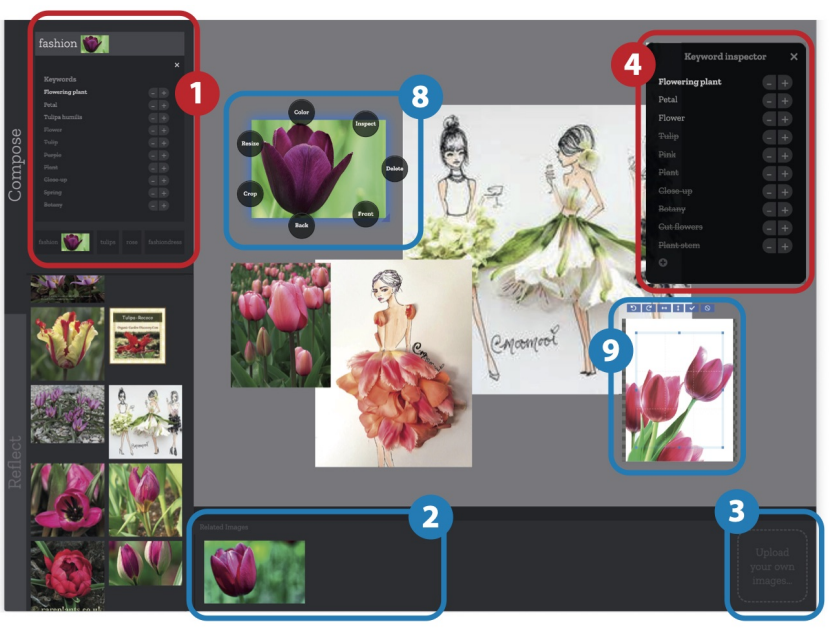
SemanticCollage digital mood board (DIS’20) [Paper][Video]
Koch et al. DIS’20, SemanticCollage (CHI’19) is a system that models layout generation as an optimization-driven process guided by semantic groupings of UI elements (e.g. related functions or meanings). Given UI content annotated with semantic tags, the model proposes new layouts by clustering semantically related items and placing them in coherent visual groupings to improve usability.

Layout as a Service (LaaS): A Service Platform for Self-Optimizing Web Layouts [Paper]
Laine et al. ICWE’20: Introduces LaaS, a platform for automatic web layout optimization using constraint-solving and feedback loops. It treats layout generation as a continuous optimization service, enabling web pages to adapt dynamically to content and user metrics.
In: Proc. ICWE’20, 2020.
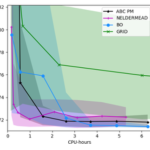
Parameter Inference for Computational Cognitive Models with Approximate Bayesian Computation (Cognitive Science 2019) [Paper][Code&Data]
Kangasrääsiö et al. CogSci’19 introduces a method for parameter inference in cognitive models using Approximate Bayesian Computation and Bayesian Optimization. The approach simulates model outputs under varied parameters, measures discrepancies to observed data, and estimates approximate posteriors without closed-form likelihoods—offering efficient, uncertainty-aware parameter fitting for simulation-based cognitive models.
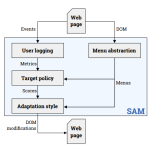
SAM: self-adapting menus on the web [Paper][Code&Data]
Gobert et al. IUI’19: Presents SAM, a method for building self-adapting web menus that learn from user behavior. The system dynamically reorders and highlights menu items to improve accessibility and navigation speed.
In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces: Companion, pp. 75–76, ACM 2019.
Ability-Based Optimization of Touchscreen Interactions [Paper]
Todi et al. IUI’18: Proposes a visual learning model that predicts how users adapt to new interface layouts. The model explains visual learning effects and supports layout restructuring that accelerates user familiarization.
In: IEEE Pervasive Computing, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 15–26, 2018.

Activation Improves Rapid Button Pressing (CHI’18) [Paper]
Kim et al. CHI’18: Impact Activation Improves Rapid Button Pressing provides an empirical dataset on rapid button-pressing tasks comparing traditional activation timing vs “impact activation” (i.e. triggering at the maximal impact depth). It includes per-participant timing accuracy, success rates, and asynchrony across conditions for a physical button and a touch-sensor version. The dataset is shared via the project page.
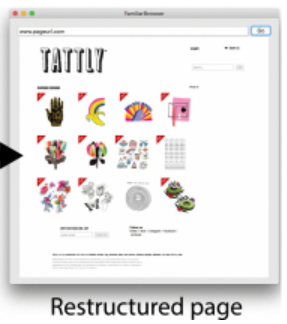
Familiarisation: Restructuring Layouts with Visual Learning Models [Paper]
Oulasvirta et al. UIST’18: Presents AIM, a computational toolkit and web service for automatic GUI evaluation. It provides quantitative metrics (e.g., efficiency, clarity, aesthetics) for rapid comparison of interface designs.
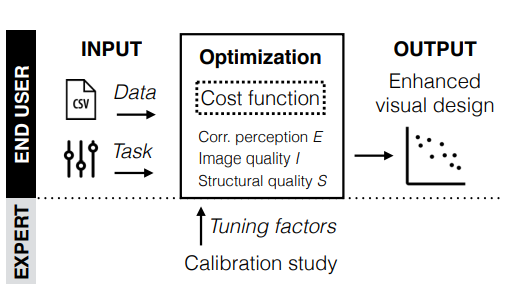
Towards Perceptual Optimization of the Visual Design of Scatterplots [Paper]
Micallef et al. TVCG’17: Develops a perceptual model predicting how visual features (e.g., density, overlap) affect scatterplot readability. The model supports automatic tuning of scatterplot parameters to maximize visual clarity and perceptual accuracy.
In: IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, vol. PP, no. 99, pp. 1-1, 2017, ISSN: 1077-2626.

Computational Support for Functionality Selection in Interaction Design [Paper]
Oulasvirta et al. TOCHI’17: Introduces an integer programming–based method to assist designers in selecting which functions to include in an interface. The tool models trade-offs among usability, functionality coverage, and task efficiency to optimize design decisions.
In: ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction (TOCHI), vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 34, 2017.
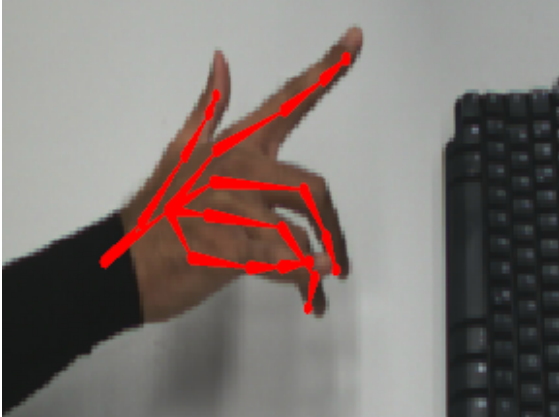

Real-time Hand Tracking Using a Sum of Anisotropic Gaussians Model [Paper]
Sridhar et al. 3DV’14: Introduces a real-time 3D hand-tracking model using anisotropic Gaussian representations. The model accurately captures hand poses and movements, enabling natural mid-air interaction.
In: Proc. 3DV, 2014.
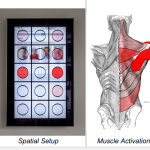
Movexp: A versatile visualization tool for human-computer interaction studies with 3D performance and biomechanical data [Paper]
Palmas et al. VIS’14: Introduces Movexp, a visualization tool for analyzing 3D motion and biomechanical data. The method integrates kinematic and muscle activation data to help researchers visually interpret complex interaction movements.
In: Proc. VIS’14, IEEE, 2014.

Improvements to keyboard optimization with integer programming [Paper]
Karrenbauer & Oulasvirta UIST’14: Improves an integer programming optimization framework for designing keyboard layouts. Enhancements reduce computational complexity and enable multi-objective optimization (speed, accuracy, learning).
In: Proc. UIST’14, pp. 621–626, ACM 2014.
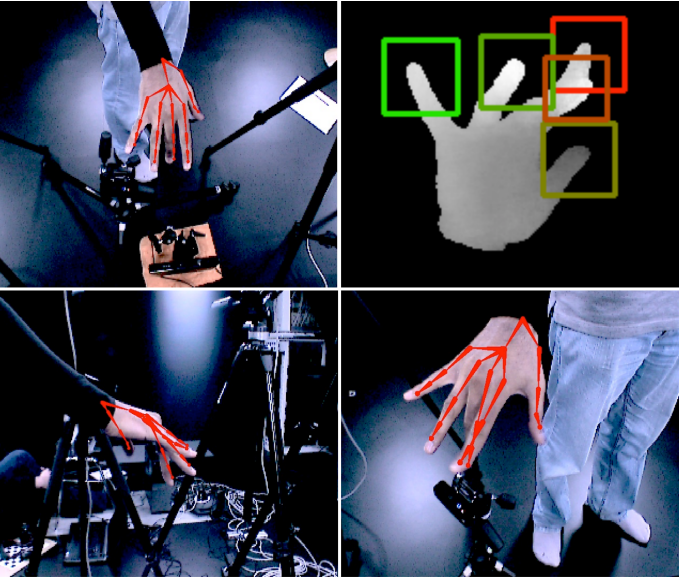
Interactive Markerless Articulated Hand Motion Tracking Using RGB and Depth Data [Paper][Video]
Sridhar et al. ICCV’13: Proposes a markerless hand-tracking model that combines RGB and depth data to reconstruct 3D hand poses. Enables detailed, real-time motion tracking for interaction without gloves or markers.
In: Proc. ICCV’13, pp. 2456–2463, IEEE 2013.
Menuoptimizer: Interactive optimization of menu systems [Paper][Video]
Bailly et al. UIST’13: Presents MenuOptimizer, an interactive tool that uses optimization algorithms to improve menu layout design. It helps designers balance speed, accuracy, and recall through iterative, data-driven exploration.
In: Proc. UIST’13, pp. 331–342, ACM 2013.